Difference between greenhouse effect and global warming venn diagram 144699
Key Difference Global warming is when the average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere and the oceans rise Greenhouse effect is the retention of the heat by the greenhouses gases on the surface of the Earth, allowing the planet's temperature to rise So the idea that burning fossil fuels causes an enhanced "greenhouse effect" needs to be taken seriously But in seeking to understand recent warming, we also have to consider the natural factors that have regularly warmed the climate prior to the industrial revolution and, indeed, prior to any human presence on the earthGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly
Ppt Global Warming And Climate Change Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Difference between greenhouse effect and global warming venn diagram
Difference between greenhouse effect and global warming venn diagram-The mechanism that produces this difference between the actual surface temperature and the effective temperature is due to the atmosphere and is known as the greenhouse effect Earth's natural greenhouse effect makes life as we know it possible However, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests, haveAdditional warming is commonly referred to as Greenhouse Warming Greenhouse Warming is global warming due to increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases (eg, carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, etc), whereas Global Warming refers only to the observation that the Earth is warming, without any



Frontiers Messaging On Slow Impacts Applying Lessons Learned From Climate Change Communication To Catalyze And Improve Marine Nutrient Communication Environmental Science
The Earth cools down by giving off a different form of energy, called infrared radiation But before all this radiation can escape to outer space, greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb some of it, which makes the atmosphere warmer As the atmosphere gets warmer, it makes the Earth's surface warmer, too Learn more about radiationIn order to compare the heating effect of different greenhouse gases, scientists have calculated a global warming potential for each one The global warming potential takes into account the amount of radiation that the gas absorbs and the wavelength at which it absorbs"Global warming" refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere "Climate change" refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time – including precipitation, temperature, and wind patterns
The main effect that causes global warming is the greenhouse effect as I said before, which is a phenomenon referred to absorption by certain atmospheric gases— mainly H2O, followed by CO2 and O3— part of the energy that the ground emits, as a In short it is the natural process that warms the Earth's surface The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouse Picture this a greenhouse is so successful at growing plants yearround, even when it's too cold outside for some An enhanced greenhouse effect from CO2 has been confirmed by multiple lines of empirical evidence Satellite measurements of infrared spectra over the past 40 years observe less energy escaping to space at the wavelengths associated with CO2 Surface measurements find more downward infrared radiation warming the planet's surface This provides a direct, empirical causal link between
This greenhouse effect, which is probably better described as warming produced by heattrapping gases, is incredibly powerful — it returns more energy to the surface than we absorb from the Sun, and its strength is closely tied to the global5 rows Comparing Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming Global warming is the change in the climate of Whereas global warming specifically refers to the warming of the planet due to increased greenhouse gas emissions, climate change encompasses the full scope of changes caused by human activity



Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Effect And Global Warming What Is
The greenhouse effect on other planets Because the greenhouse effect is a natural process, it affects other bodies in the solar system, too And, inThe greenhouse effect and global warming are two entirely different processes Definition Greenhouse Effect the name applied to the process which causes the surface of the Earth to become warmer than it would have been without an atmosphere Global Warming the increase (we think) in the magnitude of the greenhouse effect whereby the surfaceAnthropogenic climate change is defined by the human impact on Earth's climate while natural climate change are the natural climate cycles that have been and continue to occur throughout Earth's history Natural Climate Change Earth's climate has always been driven by the amount of incoming and outgoing energy Without the influence of humans, the Earth has natural cycles




Risk Management As Adaptation To Climate Change Chapter 3 Floods In A Changing Climate
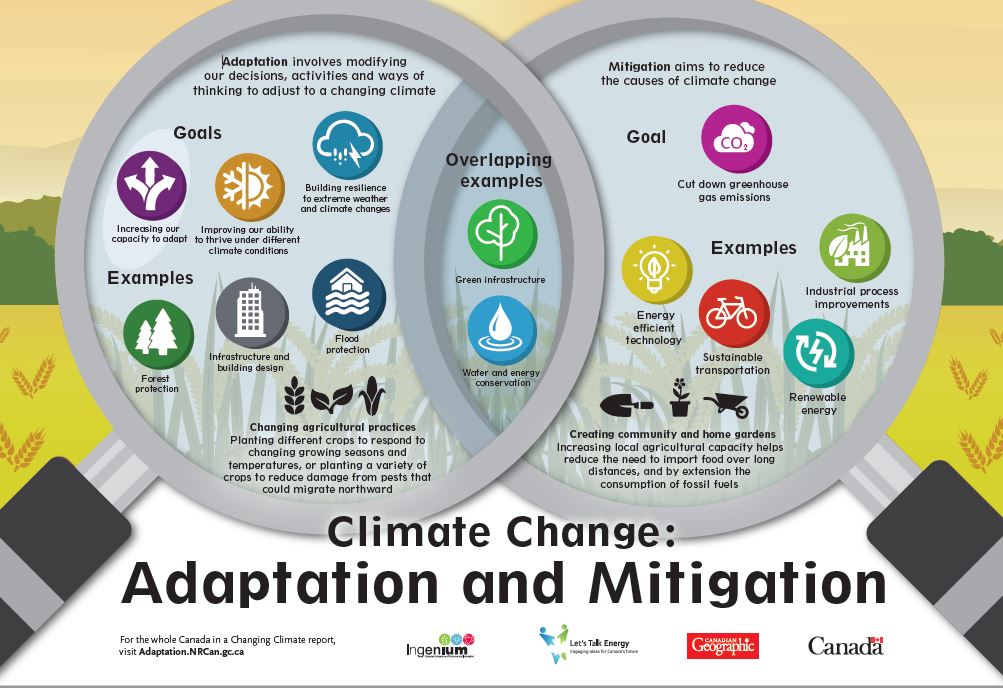



Climate Action Plan Saskatoon Ca
Impacts of a Changing Climate Each of the past four decades has been warmer than the previous one According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 16 was the warmest year on record, and the six warmest years have all been since 10 19 was the secondhottest year ever recorded, just shy of the record set in 16 Rising global temperatures threaten The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesGreenhouse gases (such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons CFCs) absorb infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and radiate it back to the surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Though the recent rise in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is arguably the main factor affecting global warming, other factors are




Global Warming Vs Greenhouse Effect Follow Green Living



2
Warmer oceans—a product of the greenhouse effect—could also decrease the abundance of phytoplankton, which grow better in cool, nutrientrich waters This could limit the ocean's ability to take carbon from the atmosphere through the fast carbon cycle On the other hand, carbon dioxide is essential for plant and phytoplankton growth Life on the earth has been possible because of this natural greenhouse effect which is due to water vapour and small particles of water present in the atmosphere Together, these produce more than 95 percent of total greenhouse warming Average global temperatures are maintained at about 15°C due to natural greenhouse effectThis breaks the equilibrium maintained by the greenhouse effect, resulting in an increase in temperature of our earth's atmosphere Simply, global warming refers to an increase in the earth's temperature Global warming is a major problem that the world is facing today




Ppt Global Warming And Climate Change Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




1 What Is The Difference Between Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming A B C 2 What Are The Brainly Ph
Global Warming Venn Diagram Directions Answer the question below using the Venn Diagram to record what people on both sides of the global warming debate say about human responsibility for this issue Be sure to note specific facts that support the different perspectives, and use the back of this paper to record more indepth details as neededLESSON PLAN GLOBAL WARMING Lesson Objectives By the end of this lesson, students will 1 Form definitions of the greenhouse effect based on prior knowledge, class discussion, and viewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3When fossil fuels burn, they produce greenhouse gases that are having a global impact on temperature and weather systems Find out about how greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane work




Furthermore I Want You To Compare And Contrast Climate Change From Global Warming Using The Venn Diagram




1 5 What Strategies Can Be Used To Address Climate Change A At An International Level B By Governmental Action C By Pressure Groups And Individuals Ppt Download
Define greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earthThe greenhouse effect The diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surfaceWorldwide scientists observe weather conditions at thousands of stations every day of the year, venn diagram global warming and greenhouse effect greenhouse effect and global warming today at the down of 21st century together with the th century especially the second half is the time when earths environment
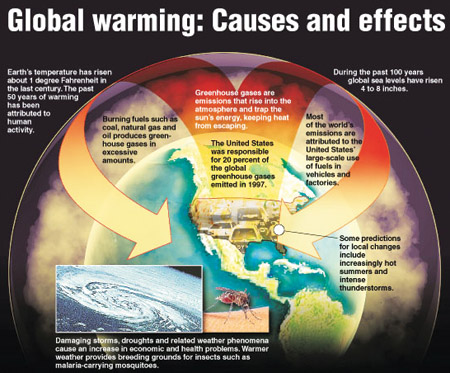



Global Warming Causes And Effects
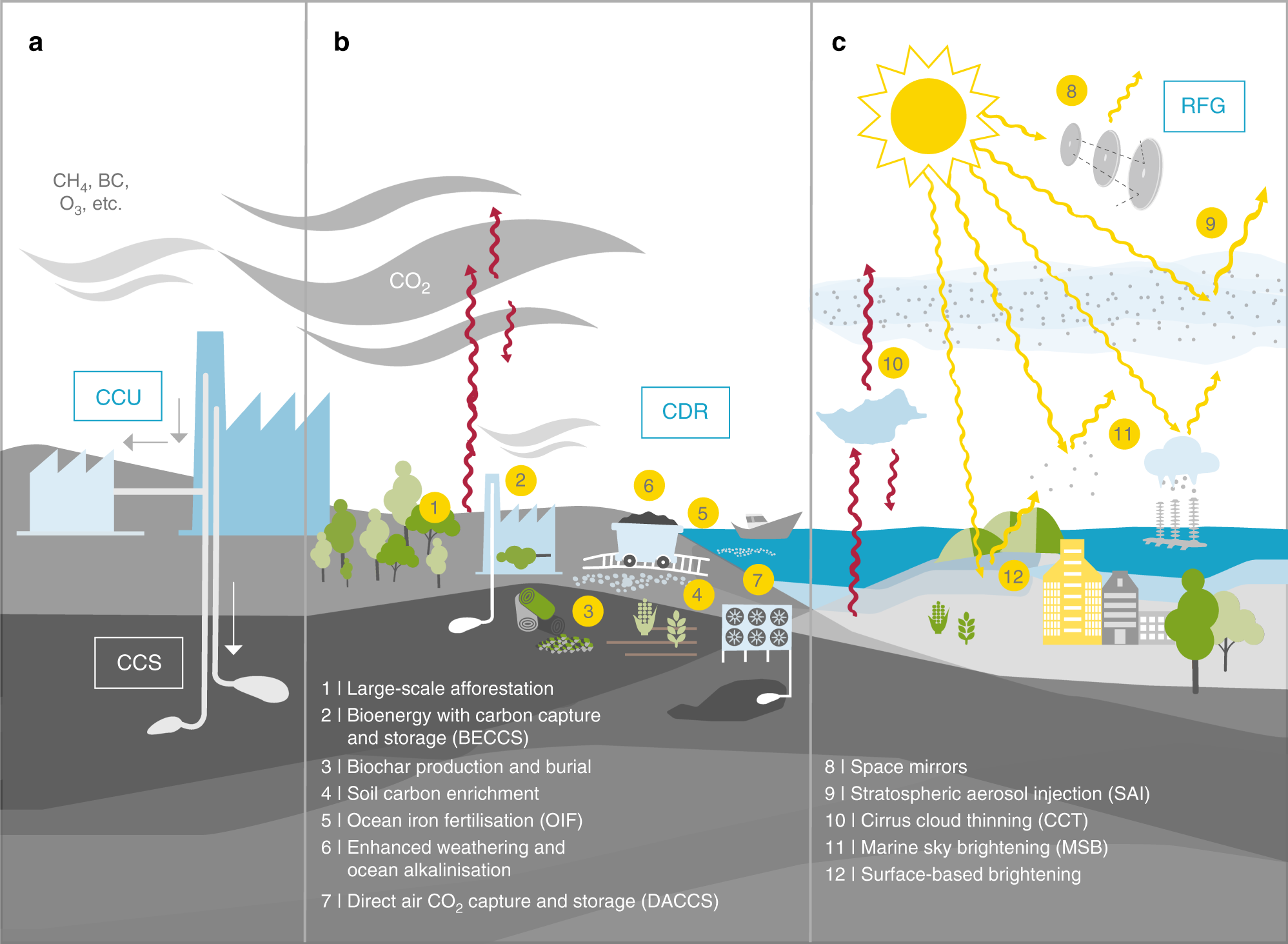



Evaluating Climate Geoengineering Proposals In The Context Of The Paris Agreement Temperature Goals Nature Communications
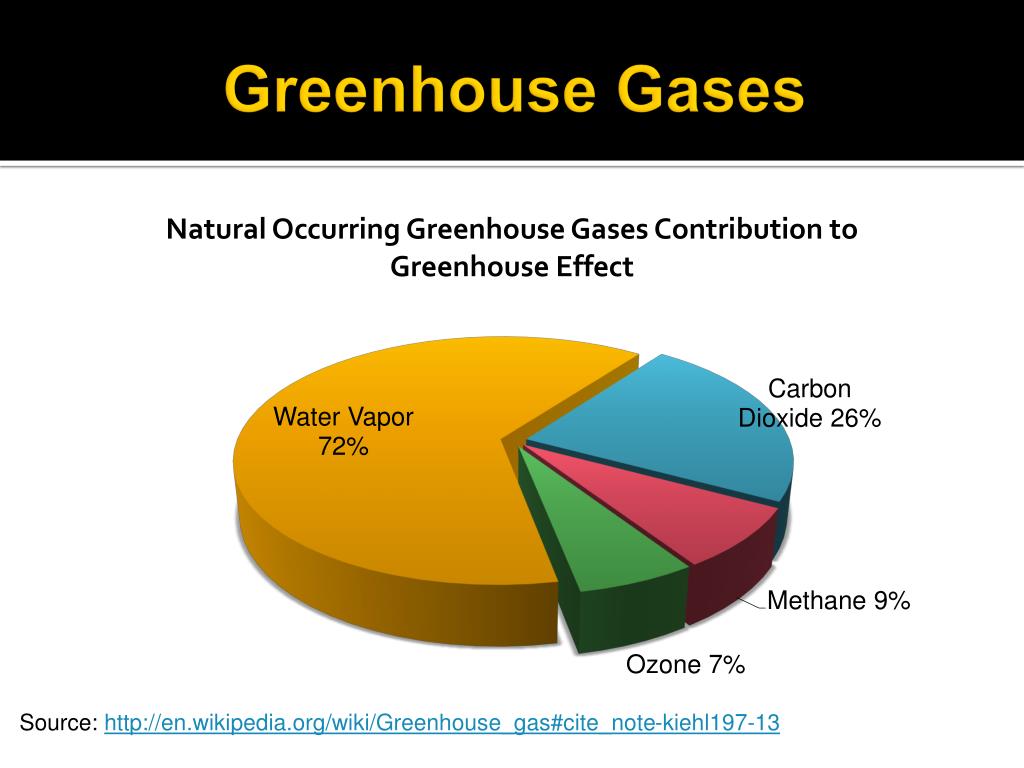
Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planet Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect (see also the graph about radion transmitted by atmosphere below) About 70 to 75% of the solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and reaches the Earth This solar radiation is absorbed on the Earth surface, which warms up the Earth surface When a body is warmer than its environment, it emits Some regions may welcome warmer temperatures, but others may not Warmer conditions will probably lead to more evaporation and precipitation overall, but individual regions will vary, some becoming wetter and others dryer A stronger greenhouse effect will probably warm the oceans and partially melt glaciers and other ice, increasing sea level
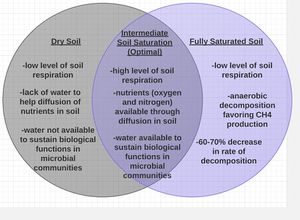



The Effects Of Global Climate Change On Soil Respiration Microbewiki




Global Warming Powerpoint Download Global Warming Ppt
Comparisons Both processes contribute to Earth's temperature/global warming Same amount of heat energy is produced by the sun & reaches the atmosphere Sun's production of energy is a major role in greenhouse and enhanced greenhouse effect CO2 plays a major role in existence of both processes CO2 & other gases block transmission of long wavelength radiationStudents explore climate change and global warming with multimedia They create a model of the greenhouse effect and then refine their findings using a demonstration and interactive Next, students research and diagram carbon sources and sinks Finally, they organize and analyze data to draw evidencebased conclusions regarding atmospheric carbon concentrations and localThe Science of Global warmingthe Greenhouse condition is over 100 years old and is not 'exotic' but basic science The science is solid and basic physics The doubt comes from what some believe is the human imprint to warming which actually has been very strong increased industrialization shows the burning of fossil fuels to have increased CO2 levels to nearly 400ppm



Weather And Climate Science Learning Hub



Solved Instructions Construct A Venn Diagram List Down Several Causes Of Climate Change On The Other Circle Enumerate The Different Impacts O Course Hero
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofLinks Between Ozone Depletion and the Greenhouse Effect The same gases which deplete ozone in the stratosphere contribute to the 'greenhouse effect' while they reside in the troposphere, or lower atmosphere Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which deplete ozone, are currently estimated to contribute about 15% of the annual increase of total global "Global warming" refers to the longterm warming of the planet Global temperature shows a welldocumented rise since the early th century and most notably since the late 1970s Worldwide since 10, the average surface temperature has risen about 1 °C (about 2 °F), relative to the midthcentury baseline (of ) This is on top of about an additional 015 °C of warming from between



Venn Diagram Climate Change Weather Png 1936x1640px Watercolor Cartoon Flower Frame Heart Download Free



Gmd Multi Variate Factorisation Of Numerical Simulations
The key difference between global warming and greenhouse effect is that global warming is the average rise in temperature near the surface of the earth whereas greenhouse effect pertains to increased concentration of gases within the atmosphere of the earth Global warming and greenhouse effect have been topics of heated discussion amongLabel one end of the room "Sun" and the other end "Earth" "Heat" students should stand at the "Sun" end of the room while the "Greenhouse Gases" students stand in the middle of the room Everyone else sits and watches until their turn Remind learners that the Sun produces heat that reaches the Earth's surfaceHuman activities contribute to global warming by increasing the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as




Alpine Vegetation In The Context Of Climate Change A Global Review Of Past Research And Future Directions Sciencedirect




Global Warming Powerpoint Download Global Warming Ppt
There are both links and major differences between ozone depletion and global warming and the way the two challenges have been handled While in the case of atmospheric ozone depletion, in a situation of high uncertainty and against strong resistance, climate change regulation attempts at the international level such as the Kyoto Protocol have failed to reduce global emissions If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a little warmer and a little warmer We may not be able to measure this effect from day to day or even year to year But over tens of years, a few degrees of warming starts causing changes For example, ice melts in the North and South Pole regions




It Must Be Global Warming That Is A Comment You Hear Frequently These Days Where Would Global Brainly Com




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming




Venn Diagram Of The Distribution Of Highly Vulnerable Countries Download Scientific Diagram



Global Warming Lesson Plan Greek Suggestion



Remember Global Warming Is A Total And Very Expensive Hoax Econbrowser




Difference Between Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




An Inconvenient Truth Then And Now What S Changed For Our Climate Since 06 Climate Reality
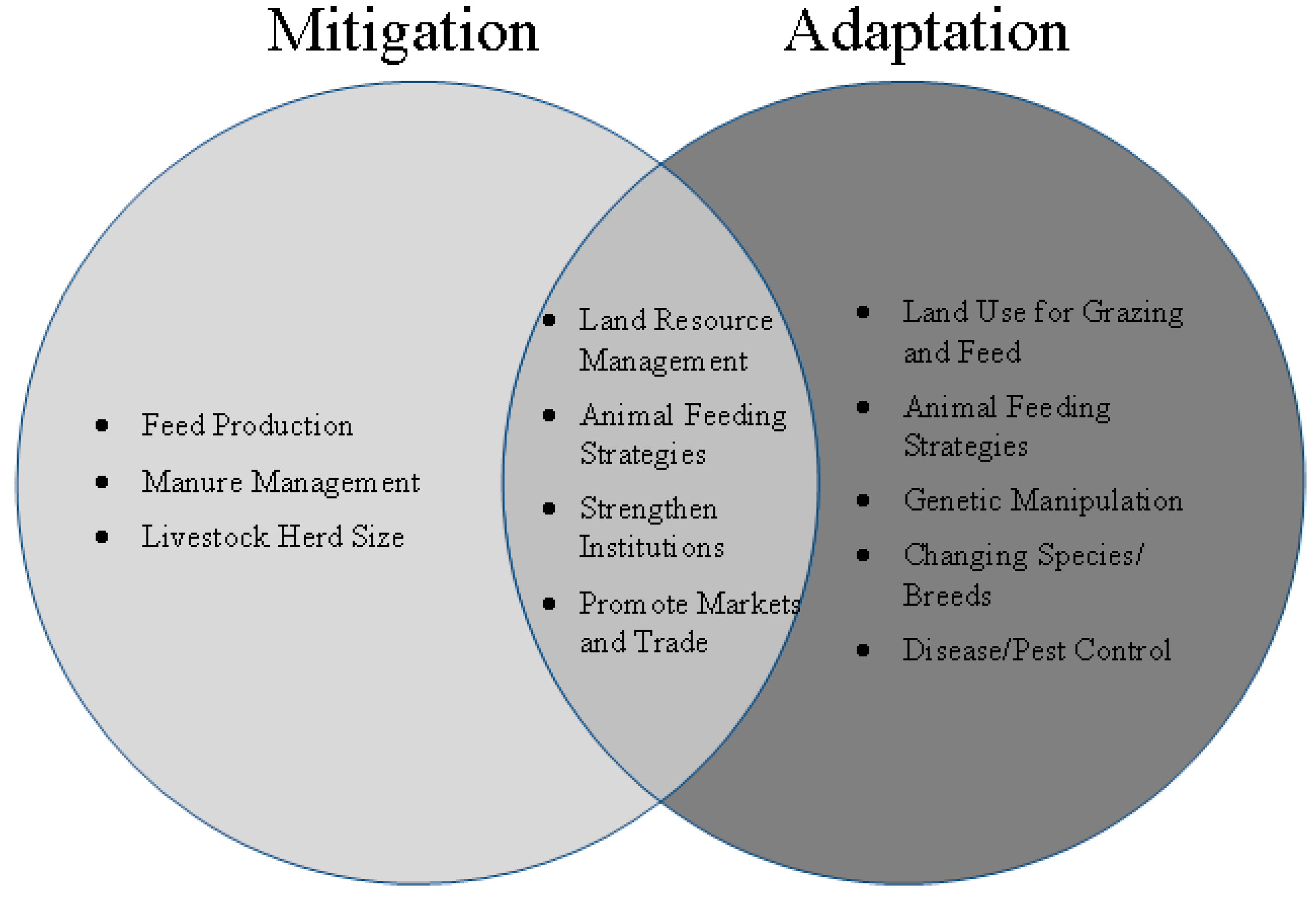



Climate Free Full Text An Overview Of Mitigation And Adaptation Needs And Strategies For The Livestock Sector Html




Adaptation To Climate Change For Water Utilities Sciencedirect




Venn Diagram Climate Change Weather Climate Community Diagrams Png Pngegg




What S The Difference Between Weather And Climate Nasa Climate Kids




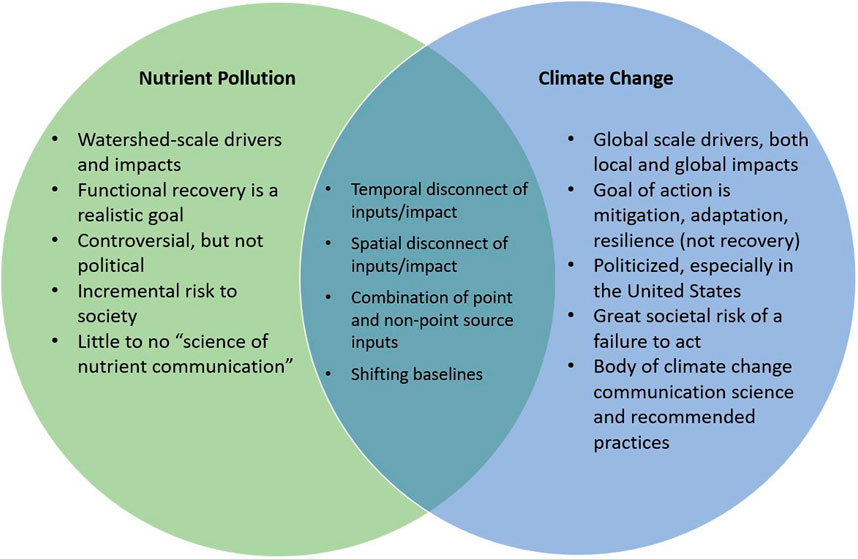
Frontiers Messaging On Slow Impacts Applying Lessons Learned From Climate Change Communication To Catalyze And Improve Marine Nutrient Communication Environmental Science




Mindmaps Directory Page 45 Of 77




Venn Diagram Of The Day On Green Heads Exploding Do Environmentalists Want Lower Or Higher Co2 Emissions American Enterprise Institute Aei



Solved Venn Diagram Climate Change In The Americasuse Figures 17 Chegg Com



Difference Between Biodiversity And Climate Change Difference Between
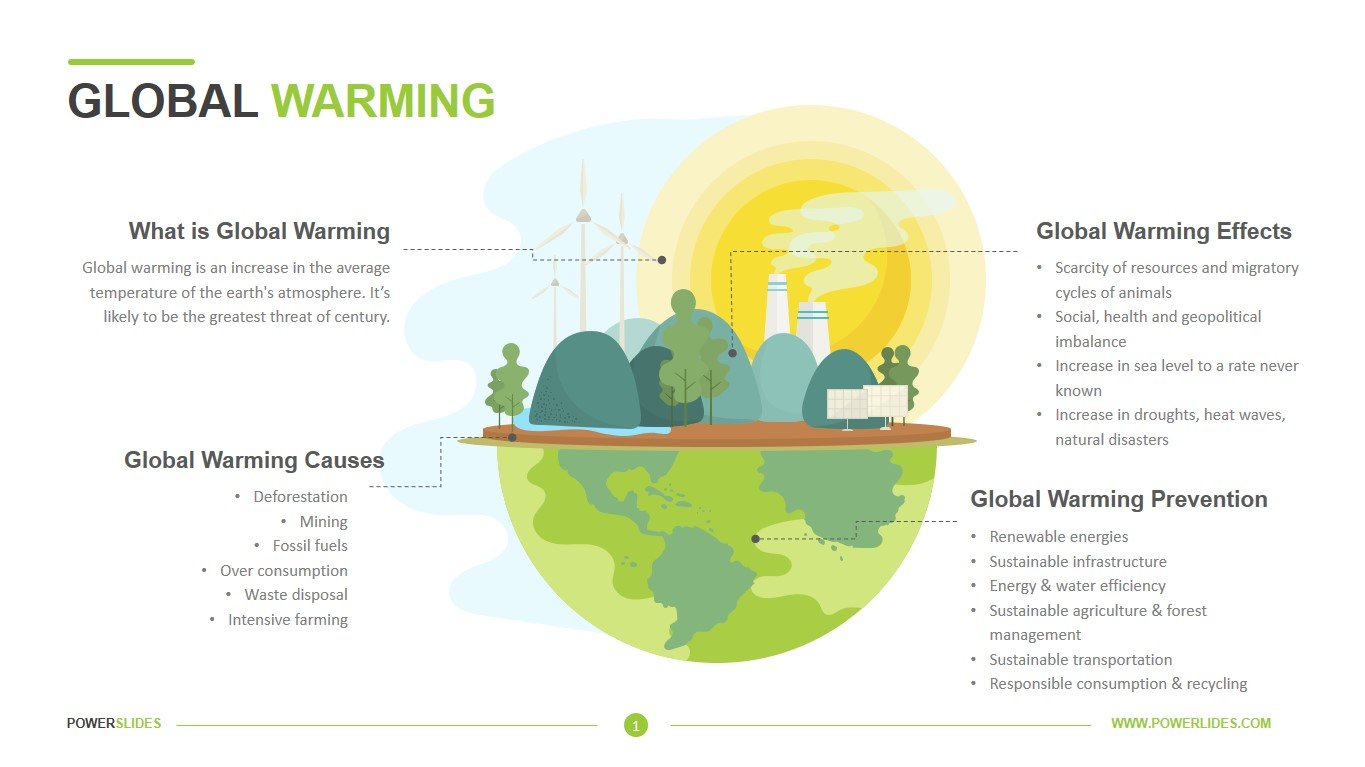



Global Warming Powerpoint Download Global Warming Ppt




Difference Between Global Warming Climate Adaptation Greenhouse Gases
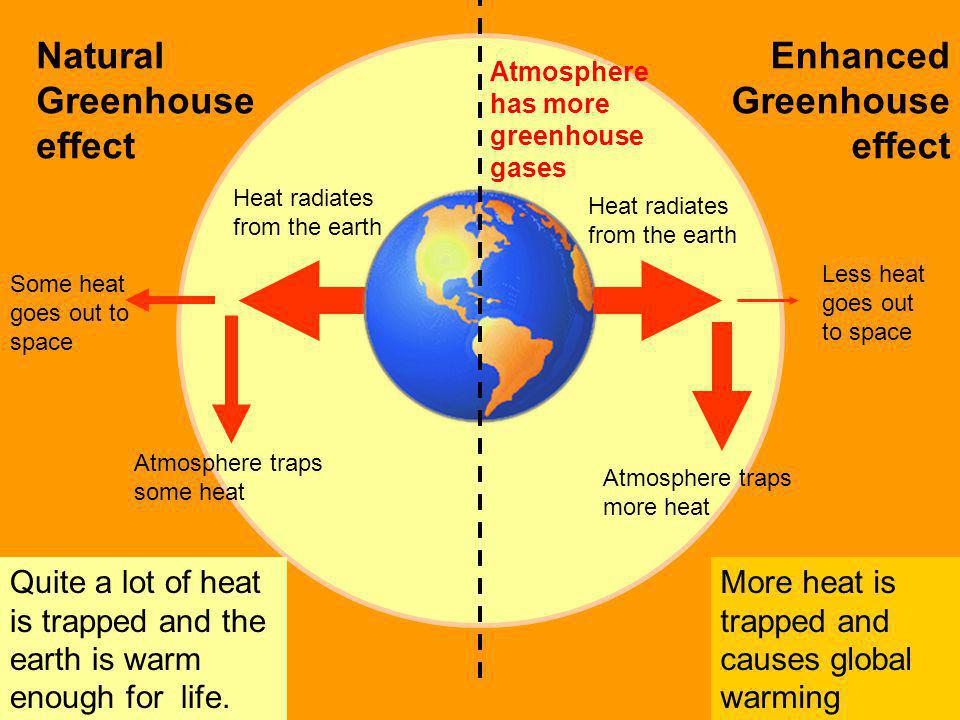



What Is Global Warming Ppt Video Online Download




Activity 3 Know My Differences And Similaritiesdirection Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Brainly Ph




Ba9a0bbfa976abf28c4b8b5 1 7067 2 Pptx Global Warming Vs Ozone Depletion Venn Diagram Compare Contrast Global Warming Caused By High Levels Course Hero




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




Climate Change Green Resilience Strategies



1




Directions Using The Venn Diagram Compare And Contrast Mechanical And Chemical Digestion Brainly Ph




Direction Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Pahelp



What Are The Similarities And Differences Between The Greenhouse Effect And An Actual Greenhouse Quora




Ppt Global Warming And Climate Change Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



What Are The Similarities And Differences Between The Greenhouse Effect And An Actual Greenhouse Quora
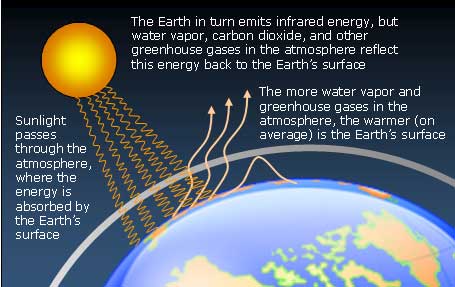



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg



Comparison Of Soil Bacterial Community And Functional Characteristics Following Afforestation In The Semi Arid Areas Peerj




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




A Venn Diagram Of The Relationships Between And Characteristics Of Download Scientific Diagram



Climate Change California Northcoast Regional Water Quality Control Board




Venn Diagram Depicting Various Economies In Green Economy Adapted From Download Scientific Diagram




What Is A Greenhouse Page Ppt Download




Paris Agreement Vs Kyoto Protocol Comparison Chart Care About Climate



Scientific Document An Ideal Goal For The Entire World Community Is To Work Toward A Sustainable Peace Or What We Can Alternatively Term Global Stability Prior To The End Of World War Ii Maintaining A Sustainable Peace Or Security For A Nation Was




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



2




Global Warming Venn Diagram Mrs Hall S Science Class



Defining Weather Global Warming And Climate Change Nonfiction Minute




Venn Diagram Comparing Opportunities And Barriers That Each Studied Download Scientific Diagram




Science 9 2 Quarter Permanos Task No 6 Une Fine Del Varmingdirections Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Greenhouse Matt And
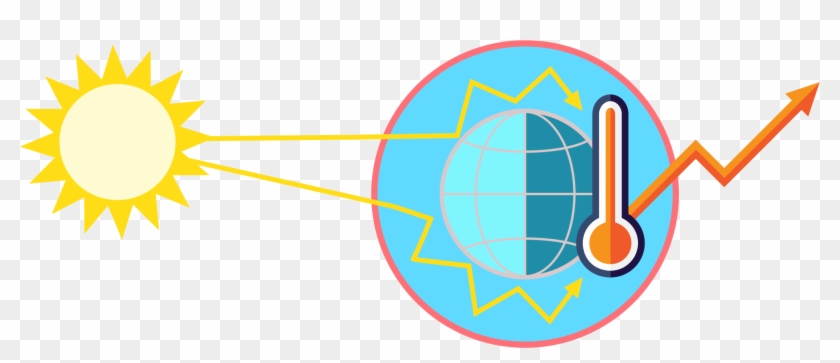



Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Calentamiento Global Vector Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download




This Annotated Venn Diagram Shows The Cyclical Nature Of Climate Download Scientific Diagram



Frontiers Defining And Managing For Healthy Vineyard Soils Intersections With The Concept Of Terroir Environmental Science




Global Warming Antimatter




Pin On Ozone Depletion




6 Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock
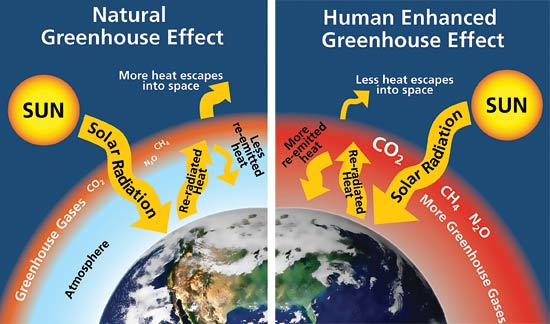



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




What Is The Difference Between Weather And Climate Oklahoma State University




Climate Change



3
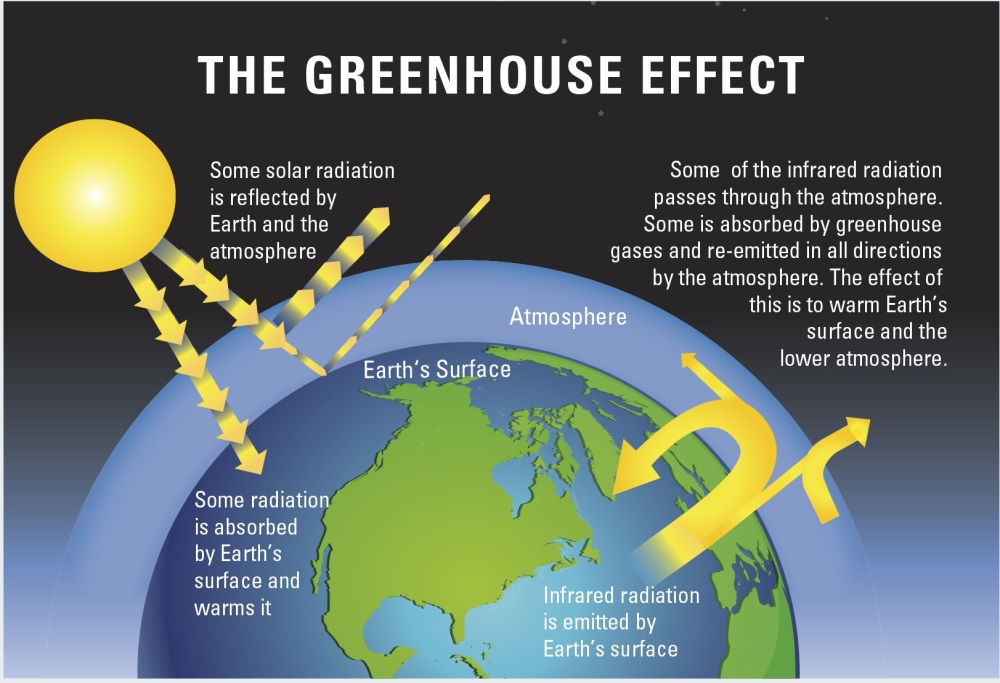



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic



Simple
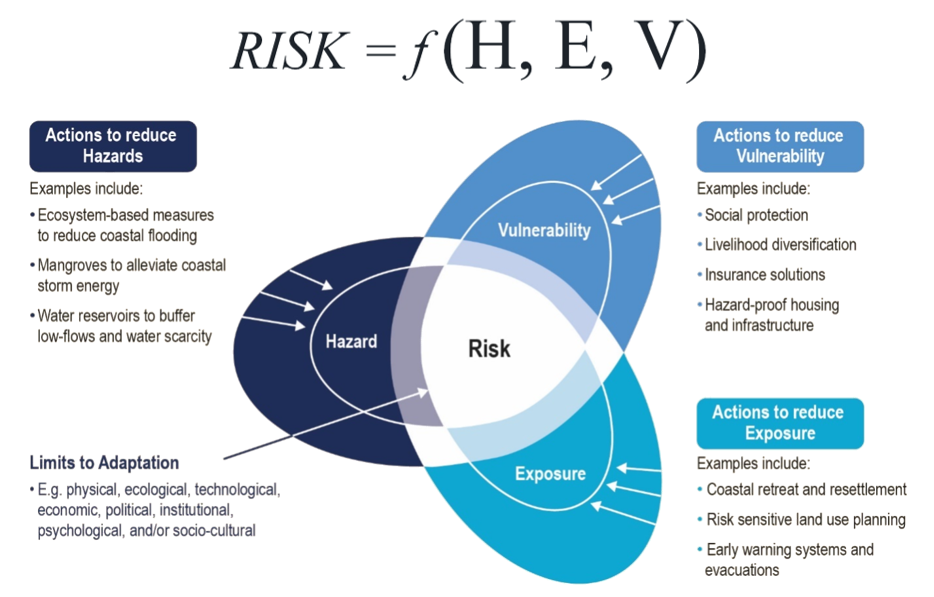



Adapting To Climate Change On Scale Addressing The Challenge And Understanding The Impacts F Asia Mega Cities Nzaia




529 Greenhouse Effect Diagram Illustrations Clip Art Istock



What Is The Difference Between Greenhouse Effects And Global Warming Quora




1 What Is The Difference Between Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming A B C 2 What Are The Similarities Of Greenhouse Effect




Anne Michelle Lee Assignment 3




Complementary Approaches To Reporting Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Direction Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming




The Climate Change Debate Authentic Learning



Difference Between Global Warming And Climate Change Pediaa Com




Greenhouse Gas Effect And Global Warming What Is



Difference Between Climate Change And Ozone Depletion Difference Between




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Global Warming Venn Diagram Canya



Global Warming Venn Diagram
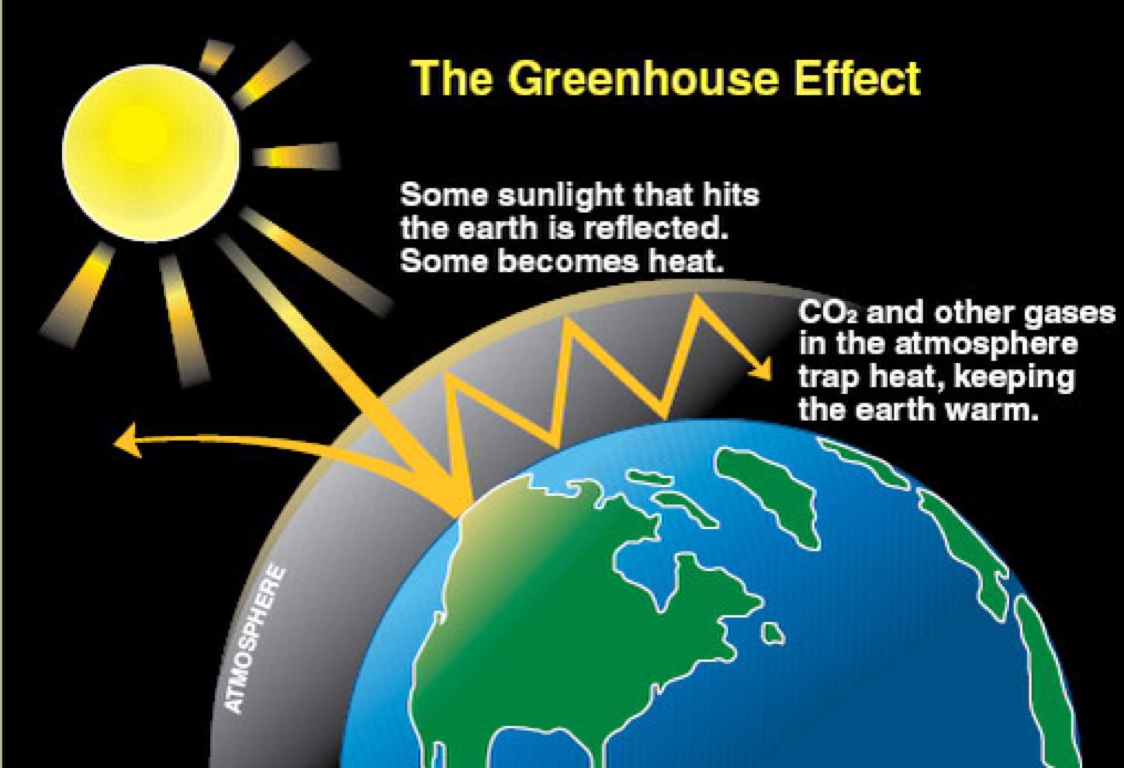



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




Venn Diagram To Show The Grouping Of The Impact Modelsthe Black Circles Download Scientific Diagram




Food Chain And Food Web In Eco System Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
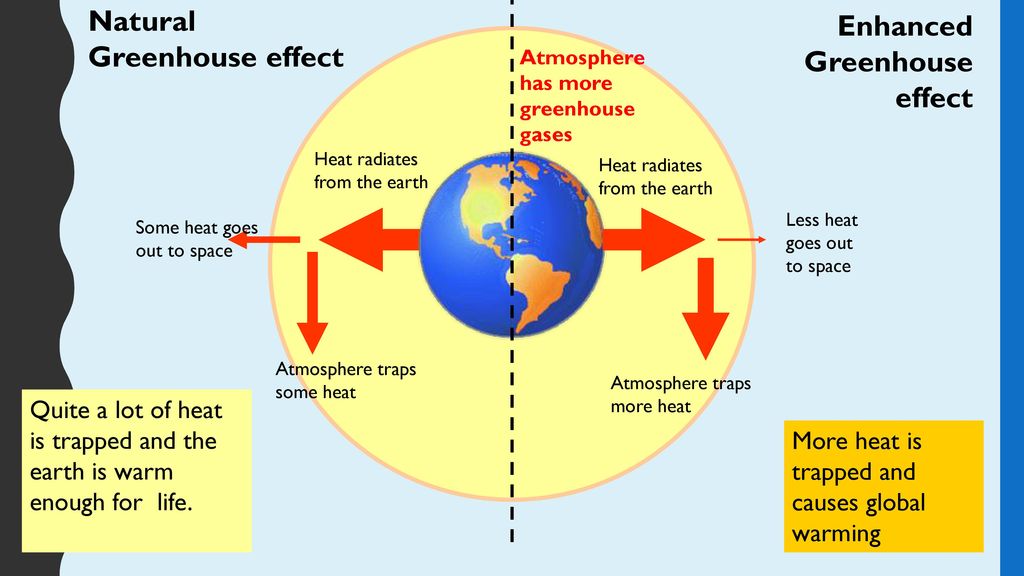



Global Warming General Studies Unit F Ppt Download




Mathematical Modelling Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Membrane Bioreactors A Comprehensive Comparison Of Two Mathematical Models Sciencedirect
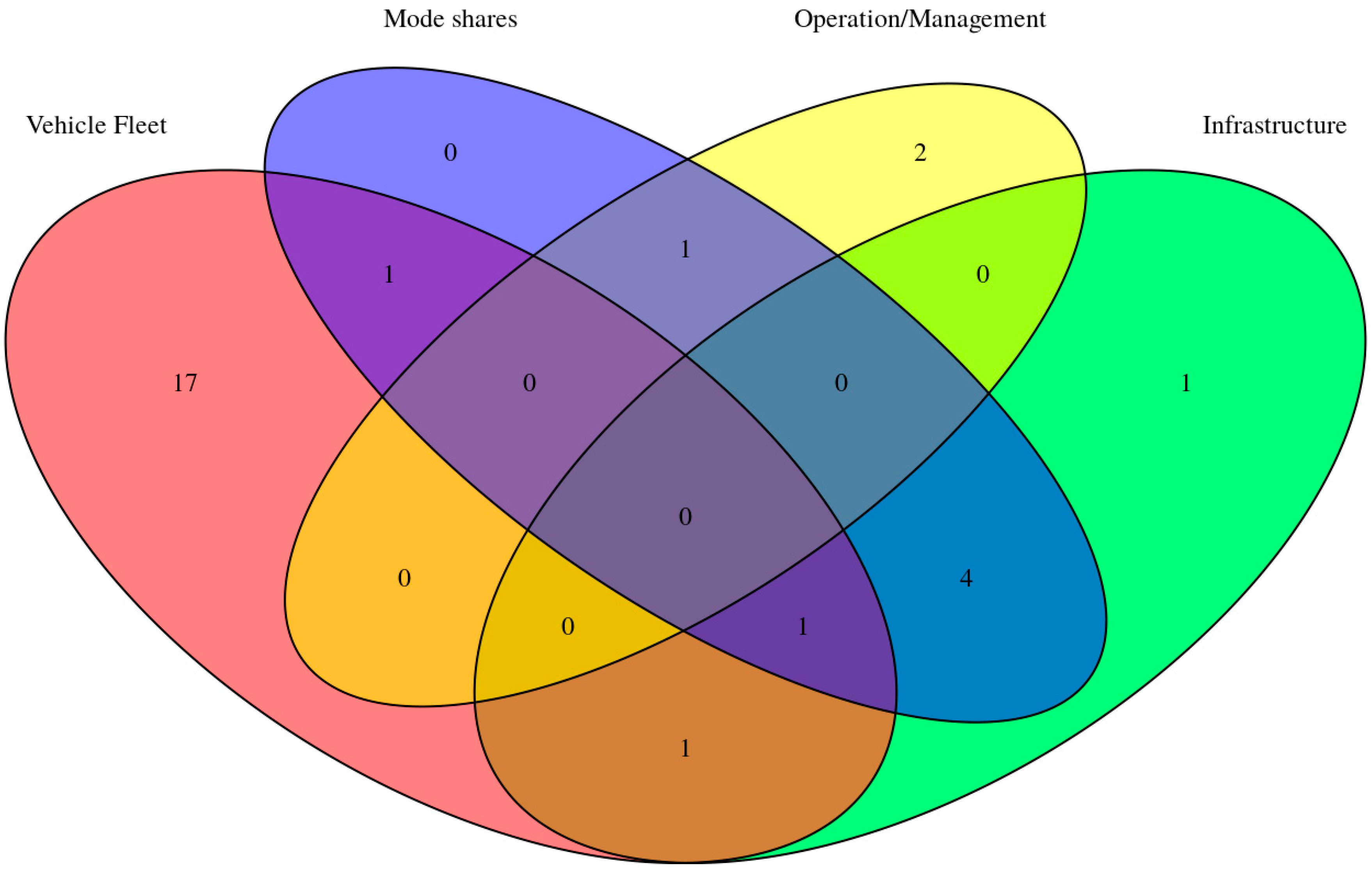



Sustainability Free Full Text Coupling Activity Based Modeling And Life Cycle Assessment A Proof Of Concept Study On Cross Border Commuting In Luxembourg Html
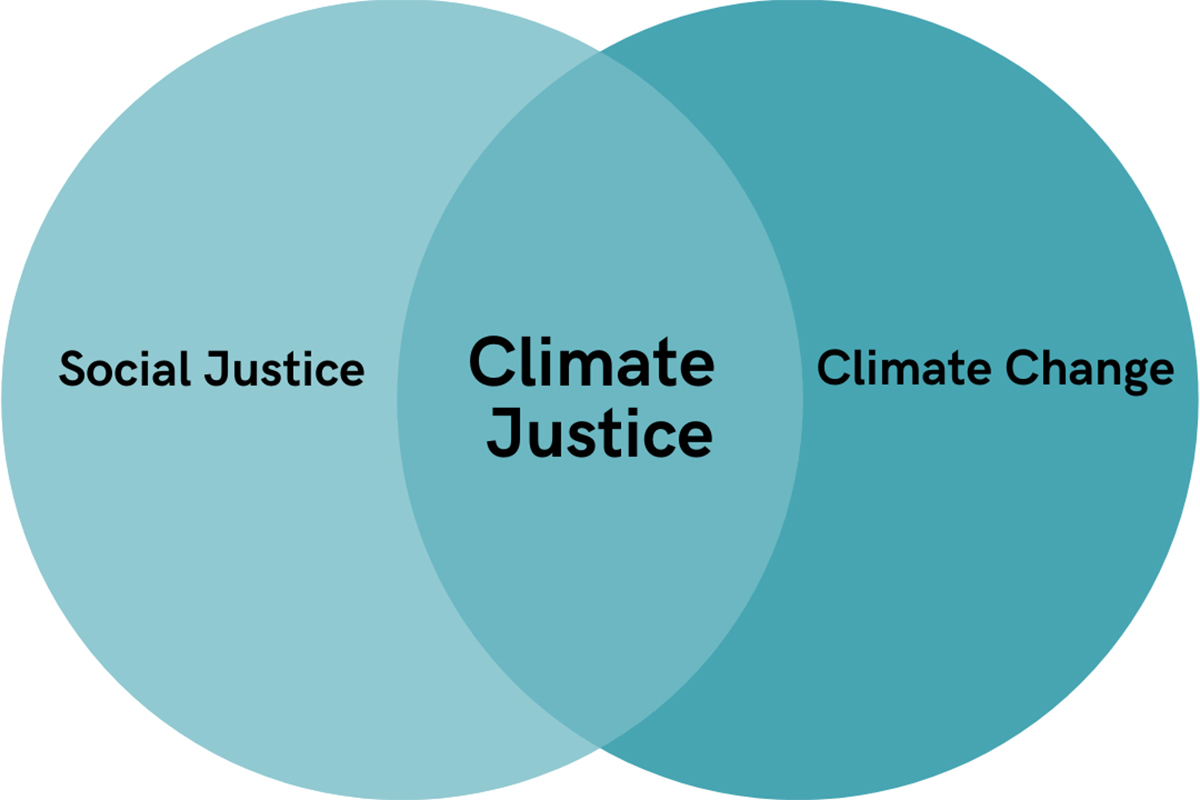



How You Can Support Climate Justice News University Of Nebraska Omaha




Venn Diagram Representing The Apparent Trend Between State That Have A Download Scientific Diagram




Climate Kids Offers Kids Clear Answers To Questions On Global Climate Change Through Sections On Weather Air The Ocea Weather And Climate Solar Energy Energy
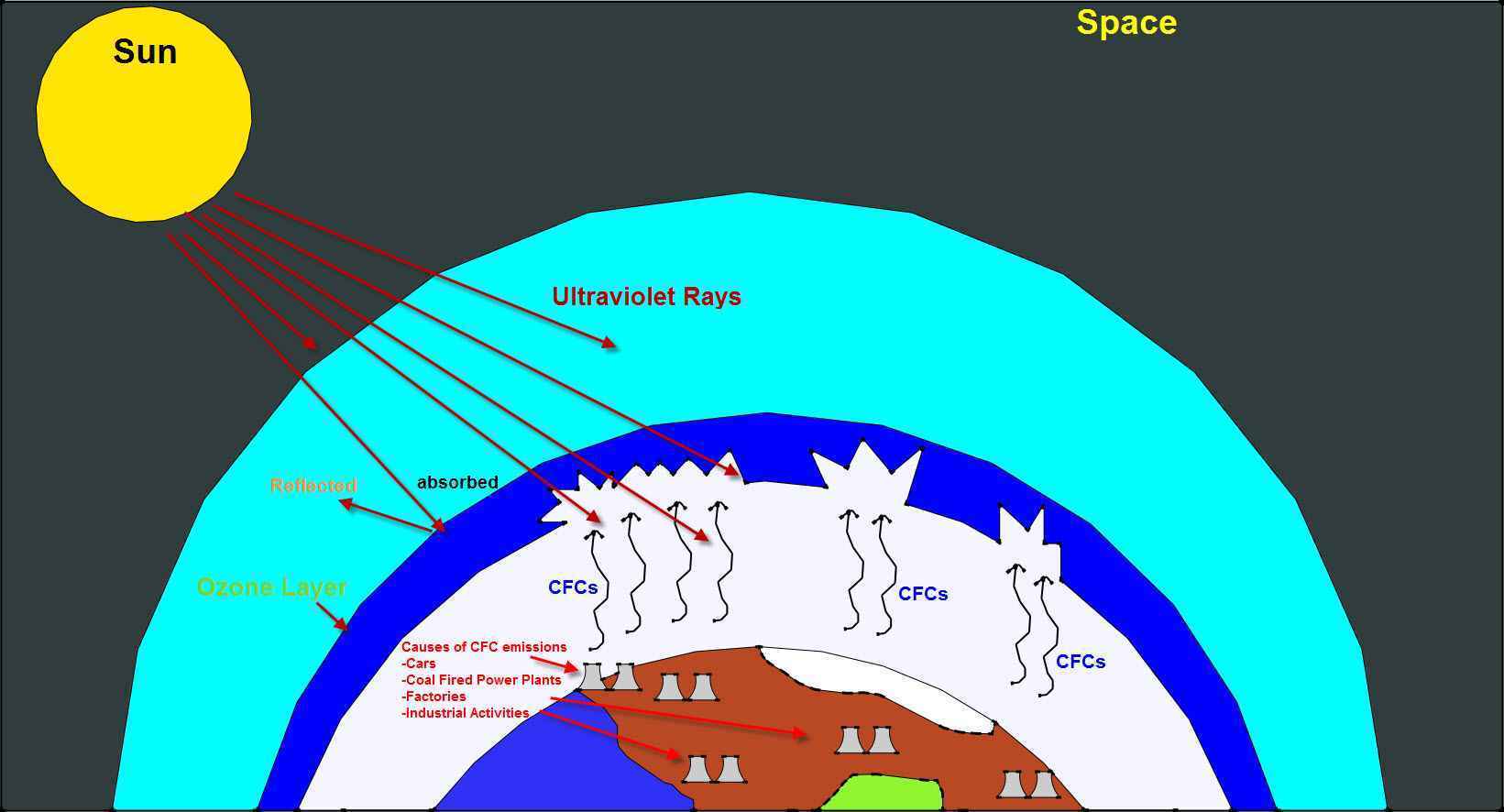



What Is The Difference Between Ozone Depletion And Global Warming Socratic




Greenhouse Gas Effect And Global Warming What Is




Direction Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Brainly Ph
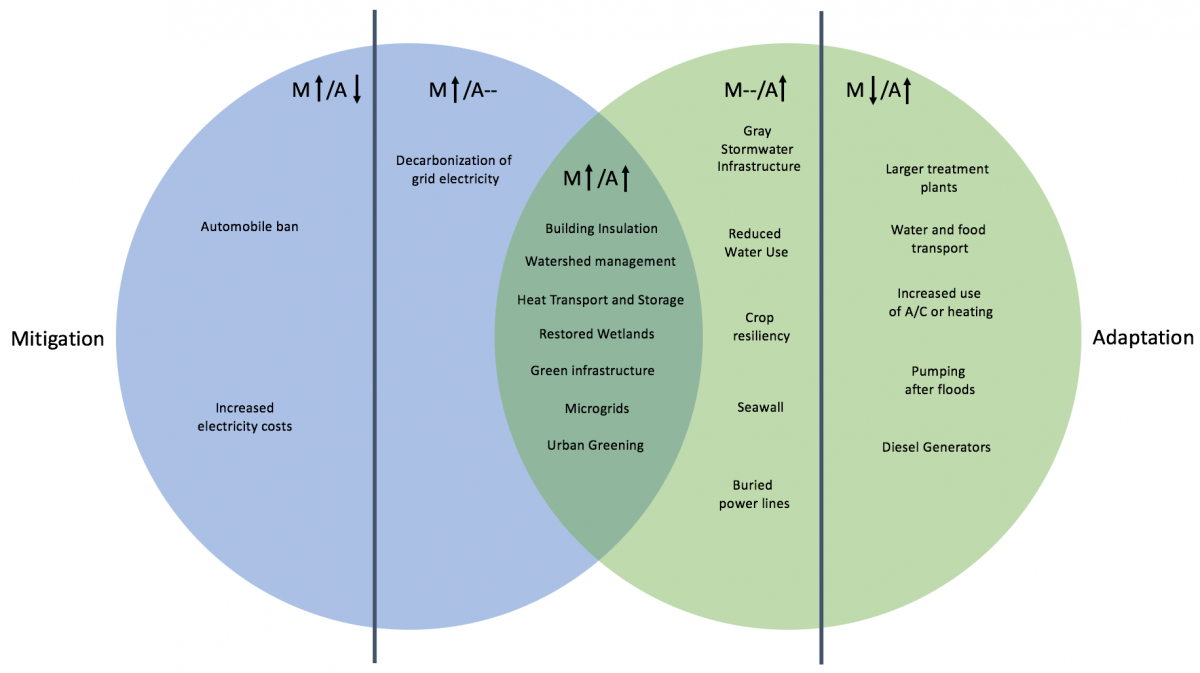



Aligning Local Logic With Global Need Kleinman Center For Energy Policy
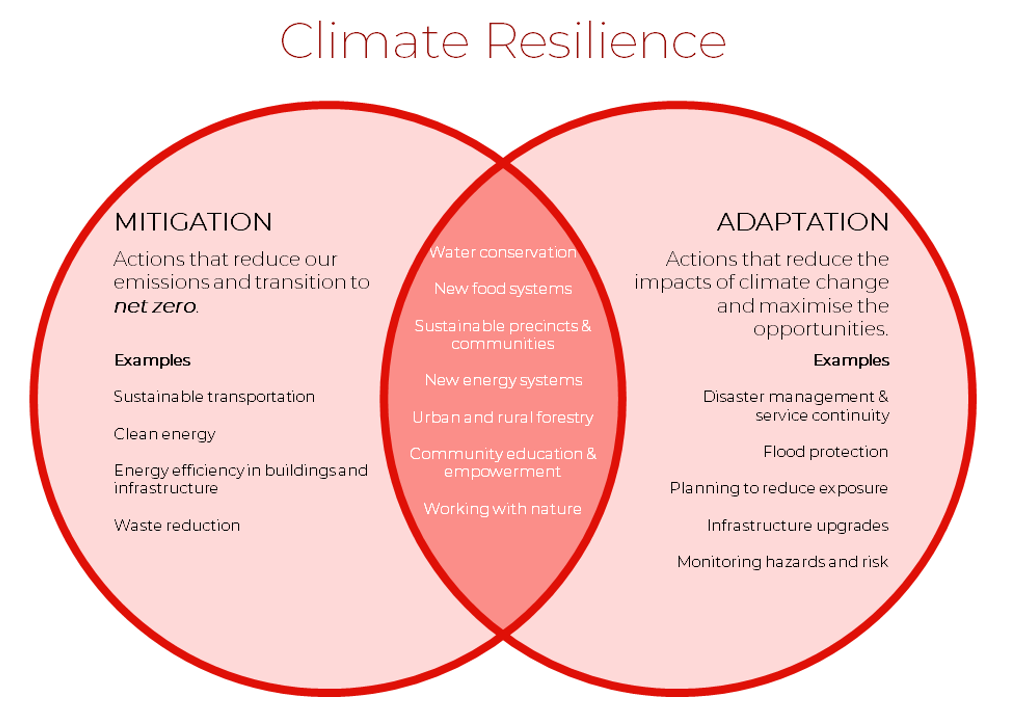



Adapting To Climate Change On Scale Addressing The Challenge And Understanding The Impacts F Asia Mega Cities Nzaia
コメント
コメントを投稿